- 404
- Home
- Remote Administration
- Employee Monitoring
- Information Security
- Features
- Live Employee Desktop
- Employee Internet Monitoring
- E-mail monitoring
- Keystroke Monitoring
- File Activity Monitoring Software
- Printed document tracking
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
- Smart rules & alerts
- Network activity monitoring
- App usage/application monitoring
- Instant Message Monitoring
- Remote Desktop Control
- Active vs. Idle Time Analysis
- Employee Productivity Tracking
- Linux terminal capture
- Nonproductive Activity Reporting
- Custom reports
- Session Recording & Metadata
- User Card
- Screen Capture
- Web-cam snapshots
- USB device control
- Data Leak Prevention (DLP)
- Voice communication recording
- File Scanner
- Software and Hardware Inventory
- Insider Threat Detection & Prevention
- Remote Employee Monitoring
- Privileged User Monitoring
- Productivity optimization
- Third Party Vendor Management
- Compliance Management, Auditing & Monitoring
- Cases
- GDPR Compliance
- For HIPAA
- For Legal
- Government & Public Sector Cyber Security
- PCI DSS Compliance & Certification
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- Energy & Utilities Sector Cyber Security
- For Financial Sector
- Retail & Ecommerce Cyber Security
- About Us
- Why Us?
- Partners
- White Papers
- Support
- Pricing
- Request demo
- Solutions
- Purchase
- Demo request
- 404
- index
- Remote Administration
- Employee Monitoring
- Information Security
- Features
- Insider Threat Detection & Prevention
- Remote Employee Monitoring
- Privileged User Monitoring
- Productivity optimization
- Third Party Vendor Management
- Compliance Management, Auditing & Monitoring
- Cases
- GDPR Compliance
- For HIPAA
- For Legal
- Government & Public Sector Cyber Security
- PCI DSS Compliance & Certification
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- Energy & Utilities Sector Cyber Security
- For Financial Sector
- Retail & Ecommerce Cyber Security
- About Us
- Why Us?
- Partners
- White Papers
- Support
- Pricing
- Request demo
- Solutions
- Purchase
- Demo request
Insider Threat Detection & Prevention
Protect Your Data and IP with StaffCop's Insider Threat Monitoring, Detection and Prevention Solution
Request demo
Insider Threats: A Major Security Risk for Many Organizations
Employees, vendors, contractors, and suppliers who have access to your organization’s internal systems are considered Insiders and any potential harm caused by them are referred to as Insider Threats. Being insiders, these users have access to the sensitive data and proprietary information including IP, trade secrets, customer and employee data, and more.
No organization is fully immune to insider threats. According to a report published by Ernst & Young and IBM, there’s a 74% perceived risk of cyber breach and insider misuse in the financial services industry; followed by 64% in consumer, retail and wholesale; 55% in tech and entertainment, and 56% in power and utilities.One of the main reasons why insider threat is so prevalent is because it’s hard to detect.
Dealing with insider threats requires a different strategy from other cybersecurity challenges because their inherent nature is different. Insiders have a significant advantage over external attackers. In addition to already having access to privileged systems, they are not only aware of their organization’s policies, procedures, and technology; they are also aware of the vulnerabilities.
No organization is fully immune to insider threats. According to a report published by Ernst & Young and IBM, there’s a 74% perceived risk of cyber breach and insider misuse in the financial services industry; followed by 64% in consumer, retail and wholesale; 55% in tech and entertainment, and 56% in power and utilities.One of the main reasons why insider threat is so prevalent is because it’s hard to detect.
Dealing with insider threats requires a different strategy from other cybersecurity challenges because their inherent nature is different. Insiders have a significant advantage over external attackers. In addition to already having access to privileged systems, they are not only aware of their organization’s policies, procedures, and technology; they are also aware of the vulnerabilities.
StaffCop: Detect, Prevent and Respond to Insider Threats with a Single Solution
StaffCop’s insider threat detection and data loss prevention solution uses real-time user activity monitoring to detect early signs of insider threats. While Its behavior-based rules engine provides active defense from all kinds of malicious insider activity like data leak and exfiltration, IP theft, fraud, industrial espionage, sabotage and other risks.
Conduct threat analysis, forensic investigation and auditing utilizing StaffCop’s unique Intelligent Session Mining with video and audio recording, complete metadata alerts, keylogging and other powerful features. Finally, extend your security coverage with built-in integration with security information and event management (SIEM) and threat analytics system if your enterprise needs it.
Conduct threat analysis, forensic investigation and auditing utilizing StaffCop’s unique Intelligent Session Mining with video and audio recording, complete metadata alerts, keylogging and other powerful features. Finally, extend your security coverage with built-in integration with security information and event management (SIEM) and threat analytics system if your enterprise needs it.
1
Real-Time User Activity Monitoring for Early Warning
Teramind monitors all user activity covering 22+ system objects like: web, apps, email, file transfers, etc. and even on-screen content (OCR) in real-time.
2
Identify and Secure Sensitive Data
Discover and identify sensitive information and StaffCop will protect them from falling into the wrong hands.
3
Behavior Analytics to Detect Anomaly
Intelligent behavior analysis can detect malicious activity and anomalies that indicate deviation from normal behavior.
4
Prevent Threats with Rules Engine
Use the powerful Policy & Rules Editor to create rules to define what constitutes insider threats. StaffCop then takes immediate actions like warn when rule violation is detected.
5
IT Forensics to Investigate Security Incidents
Video recording of all user activity, audio recording, session recording, immutable logs, alerts and optional OCR search are just a few examples of StaffCop’s powerful audit and forensic capabilities. Together they provide a vast collection of investigation data to locate the source and insider threat with pinpoint accuracy.
6
Implement Cybersecurity Best Practices and Standards
StaffCop’s insider threat detection is built on cybersecurity frameworks like NIST, ISO 27001, FISMA etc. to give you complete peace of mind knowing you are using a solution that conforms with world-class security standards. Implement GDPR, PCI-DSS, HIPAA and other compliance standards to protect sensitive data from insider threats.
7
External & Privileged User Monitoring for Extra Protection
Monitor external and privileged users like third party vendors, remote users and IT admins who have access to your critical systems to prevent sabotage or data theft.
Industry Statistics Show the Need for
Insider Threat Prevention Solutions
Insider Threat Prevention Solutions
Сolluding employees are the sources of insider threats
According to the Community Emergency Response Team, the main reasons for insider caused incidents are collusion from employees and third-parties.
48.3%+ Insider-Insider Collusion
16.75%+ Insider-Outsider Collusion
Employee privilege puts sensitive data at risk
According to a survey of 400,000 member online by Cybersecurity Insiders published on The Insider Threat 2018 report.
37% Insider-Insider Collusion
34% Increased Amount of Sensitive Data
It security pros are worried about insider threats
When asked to assess their organization’s vulnerability to insider threats, 90% of cybersecurity professionals said they felt vulnerable. Source: Cybersecurity Insiders.
90% Feel Vulnerable to Insider Threats
The average cost of insider threats is in millions
A 12-month benchmark of 159 companies found the average cost of insider threats to be $8.76 million. Source: Ponemon Institute.
$8.76M Benchmarked Average Cost of Insider Threats
StaffCop Insider Threat Prevention
Solution is Built on the NIST
Cybersecurity Framework
Solution is Built on the NIST
Cybersecurity Framework
StaffCop utilizes the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) cybersecurity framework to Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond and Recover on data breaches. Combining its powerful user activity monitoring and data loss prevention (DLP) capabilities, StaffCop is able to help organizations prevent insider threats and data breach incidents with ease.
1
Identify
Leveraging advanced fingerprinting, OCR and tagging technology, StaffCop identifies sensitive data in structured and unstructured information across organization data stores.
2
Protect
StaffCop leverages its activity monitoring and data loss prevention capabilities to defend confidential information from unauthorized access, sharing, attack and misuse.
3
Detect
StaffCop’s powerful behavior-based policy and rules engine casts a strong detection net over the entire organization, allowing for quick detection of insider threats and data breach incidents before it happens.
4
Responde
Real-time notification and immediate actions proactively defend against data exfiltration, malicious or accidental insider threats and data breaches. In case of an incident, pinpoint the exact cause and source of the incident with readily available forensic data.
5
Recover
Conduct forensic investigation with incident reports, alerts and session recordings. Identify the source and cause of a security breach so that recovery plan can be formulated fast while preventing similar future incidents.
StaffCop Insider Threat Prevention
is Your Ultimate Defense Against Insider Threats and Data Loss Incidents
is Your Ultimate Defense Against Insider Threats and Data Loss Incidents
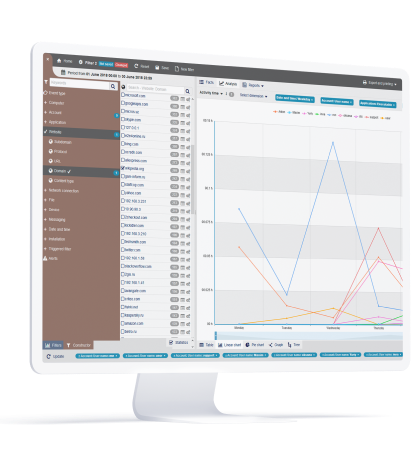
Establish Organization-Wide Visibility and Control
StaffCop visually records every action that a user makes for over 22 objects including screen, apps, websites, files, emails, etc. Each object can be configured to take into consideration what needs to be monitored and who has access to the monitored records. You can control who you want to monitor, how much you want to monitor, when and for how long. This allows for instant administrative oversight in respect to privacy requirements.
Detect and Prevent Threats Early and Automatically
First, determine what behaviors are high risk i.e. copying files to external drives, using cloud storage to share corporate files, downloading/opening files and attachments from unknown sources etc. Then, apply advanced behavior-based rules to automatically detect when users violate the rules. Utilize sophisticated anomaly rules to identify user activity outside the normal behavior. Immediately get notified about harmful user activity, lock them out from the system or take remote control of their computer before any malicious or fraudulent attempt.

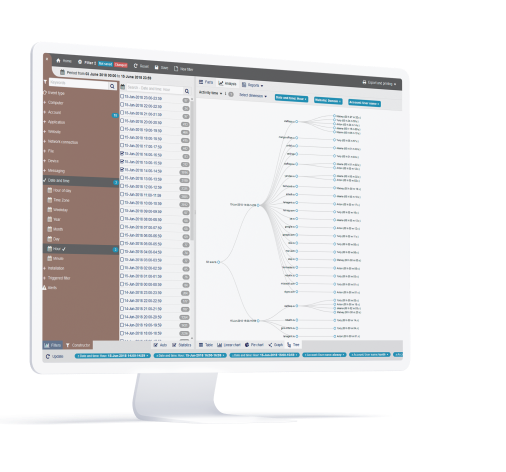
Monitor Privileged Users, Remote Users and Third-Parties to Prevent Collusion
Teramind allows organizations to create profiles for remote, privileged, external vendors and then define what information and system resources each profile can access. Further rules can be set up by behavior policies so that access to sensitive information is segregated by the organization’s security policy, or on a need-to-know basis. Rules can also be created to notify the authorities of any suspicious privileged user activity, such as unscheduled and/or unauthorized changes to system configuration, creation of backdoor accounts etc.
Investigate Threat Incidents and Conduct Forensic Analysis and Audit
Detailed alerts for all users can be viewed including any breach events and what actions were taken. Warning messages can be configured to inform the users about nonconformity as it pertains to handling sensitive data. Influence corrective behavior with on-time feedback and notifications. Session recordings and history playback can be used to view user’s desktop for audit and evidence gathering purposes.
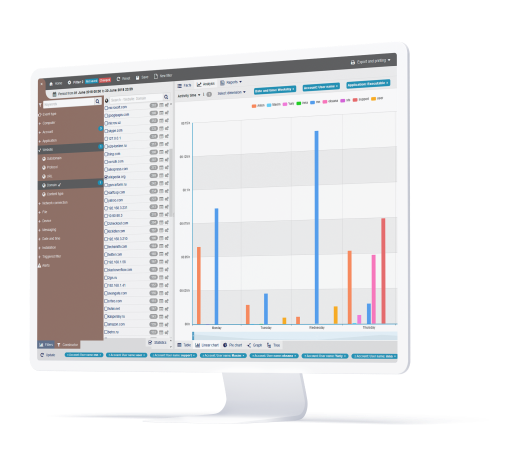
Need a More
Comprehensive Solution?
Comprehensive Solution?

Information Security
Receive the required data “on the fly”. Search by keywords and regular expressions. Record sound from microphones to hear what was happening at the moment of interest..
Try for free 
Remote Administration
View remote desktop without being notices. Take control over a workstation. Full picture of software and hardware usage. Intensity of usage and registry of states.
Try for free Recommend

Employee Monitoring
Categorize applications and web-sites into productive and unproductive. Set up different configurations for particular users, groups and departments. Compare results. ...
Try for free Flexible Deployment Options

Bare Metal
Install on bare metal from our ISO image containing Ubuntu 18.04 and StaffCop or install StaffCop packages on existing Ubuntu 18.04.

Virtual Machine
Install on any OS as a virtual machine from our ISO image, use Virtual Box, VMWare, Hyper-V or any other virtualization system. Easy administrating without risking the host machine.

Private Cloud
Use your own secure, scalable private cloud implementation including AWS, Google Cloud, Azure and more
LEARN
Documentation SUPPORT
%201.svg?v=2020-10-15T10:37:02.579Z)




